RDW is an abbreviation for Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and it’s a key blood value that informs us about how varied in size your RBCs are What Level of RDW Is Dangerous. Although it’s commonly ignored, a high RDW may signal health issues such as nutritional deficiencies or chronic diseases. Understanding when your RDW levels are typical, when they’re cause for concern and what you can do about abnormal levels can help you maintain your health. In this article we discuss the basics, find out how high is dangerous and what causes elevation, the symptoms and how to manage RDW in a straightforward, reader friendly manner.
What Is RDW
RDW quantifies size differences in RBC population. Red blood cells are normally the same size, and RDW measures the extent to which they vary in size. RDW is commonly part of a complete blood count (CBC) test, along with hemoglobin, hematocrit and other parameters. RDW alone can’t diagnose a disease, but it is a useful sign that can be used with other blood indices. A high RDW can be a sign that you are making red blood cells of many different sizes due to vitamin deficiencies, chronic illness, or bone marrow disorder. What Level of RDW Is Dangerous and Low RDW is rare but can indicate medical issues as well, he added.
Why RDW Matters in Your Blood Test
Physicians also watch RDW because it can show early signs of anemia, vitamin deficiencies and inflammatory diseases. Such as:
- Iron deficiency anemia may result in small RBCs, increasing RDW.
- A deficiency in vitamin B12 or folate can result in larger RBCs, also increasing the RDW.
- Red blood cell turnover may be affected by chronic inflammation or heart failure.
RDW enables doctors to determine the type of anemia of What Level of RDW Is Dangerous, track the progress of its treatment and detect latent health issues prior to manifestation of symptoms. The day-to-day, or even the week, monitoring of RDW trends is likely to provide more information than any single value as it may tell you if your red blood cell size variability is stable, improving, or worsening.
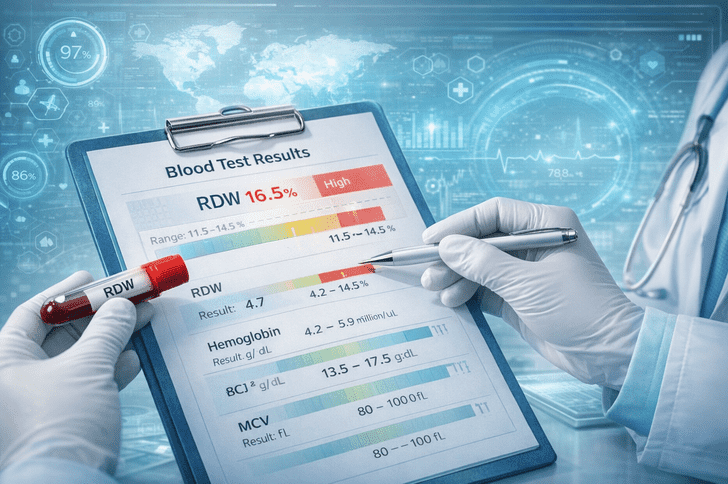
Normal RDW Range
Before you can know what harmful levels are toRDW you need to know what normal levels are:
- RDW-CV (Coefficient of Variation): 11.5% – 14.5%
- RDW-SD (Standard Deviation): 39–46 fL (lab-dependent)
Depending on the laboratory and patient’s age in what Level of RDW Is Dangerous, the ranges might slightly differ. Minor abnormalities of value do not always necessarily imply risk or danger for any patient although some form of follow-up may be indicated. Doctors may also evaluate RDW with hemoglobin, MCV (Mean Corpuscular Volume) and other CBC metrics to better understand the health of red blood cells.
What Level of RDW Is Dangerous
A high RDW level is generally a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
- High RDW (>15%): Indicates high degree of anisocytosis. Might be linked to iron deficiency anemia, cobalamin (vitamin B12) or folate deficiency, chronic inflammation, or cardiovascular diseases.
- Low RDW (<11.5%): Uncommon, but can indicate certain bone marrow diseases and long-standing anemia.
But a single abnormal test and knowing about What Level of RDW Is Dangerous is reading does not necessarily mean you have a serious problem. Physicians monitor trends and compare with other tests. Elevated RDW is very worrying when the person who has it is tired, pale, or experiencing heart palpitations. Continually abnormal results should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Causes of High RDW
High RDW may be due to one or more of the following:
- Iron Deficiency Anemia – What causes it The most common cause. Iron deficiency causes the cells to be small and hypochromic (they have less color), this also leads to a variation in size.
- Vitamin B12 or Folate Deficiency – absence of these vitamins produce megaloblasts (large RBC).
- Chronic Inflammation – Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can like interfere with red blood cell production.
- Liver or Kidney Disease – the production and life span of the red blood cells may be significantly decreased due to organ failure.
- Heart Disease – Elevated RDW is associated with cardiovascular risks, including heart failure.
Others potential contributors are chronic infections, hypothyroidism and some drugs. Because What Level of RDW Is Dangerous can contribute to help us pinpoint the underlying cause when we are looking at other blood markers.
Causes of Low RDW
Low RDW is rare but may also indicate health problems:
- Bone marrow disorders – A few disorders can cause the bone marrow to produce RBCs that are very similar in size, resulting in a low RDW.
- Chronic low-grade anemia – At times the RDW remains low in anemias even when hemoglobin values are abnormal.
- Other uncommon causes – Inherited conditions or long-standing poor nutrition.
Doctors tend to pay more attention to a high RDW when they know about What Level of RDW Is Dangerous because it is a more frequent predictor of health risks .
Symptoms Associated With Abnormal RDW
Abnormal RDW be observed through broad symptomatology, which changes according to cause of its change:
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations (in severe cases)
Since these symptoms are nonspecific in What Level of RDW Is Dangerous, people might dismiss them until routine blood tests pick up a high RDW. Early diagnosis and treatment are important.
When to Seek Medical Help
Consult a doctor if:
- RDW levels remain persistently high or low
- Accompanied by fatigue, pallor, or palpitations
- There is a history of anemia, heart disease, or chronic illness
Regular monitoring and consultation with a haematologist may assist in determining the cause. Don’t place too much stock in one wonky test result – trends over multiple tests tell you more.
How to Improve Abnormal RDW Levels
When EDW levels are abnormal, they can usually be treated, depending on the etiology.
- Iron supplementation and iron-rich foods – beef, pork, beans, spinach, cooked cereals, and cereal enriched with iron.
- Vitamin B12 and folate intake – Eggs, dairy products, leafy vegetables, enriched cereals or nutritional supplements.
- Managing chronic diseases – Manage diabetes, heart disease, or inflammation.
- Lifestyle adjustments – Diet, exercise, and not too much alcohol.
- Regular blood monitoring – When EDW levels are abnormal, they can usually be treated, depending on the etiology.
Consult a health care provider before taking any supplements or undergoing treatments.
RDW and Anemia – The Strongest Connection
RDW is especially helpful when assessing anemia because the red blood cells are impacted in different ways with the various forms of anemia. For instance, red blood cells in iron deficiency anemia are smaller and more variable in size, leading to an elevated RDW. In comparison, the red blood cells are larger and tend to be irregular in shape in a vitamin deficiency anemia (B12 or folate) presenting with a high RDW. Anemia of chronic disease usually has very little variation in the size of the red blood cells, which manifests as a RDW that is modestly elevated. When RDW values are analyzed in conjunction with other blood parameters, including MCV, hemoglobin and hematocrit, physicians are able to make a precise anemia diagnosis and suggest the best course of therapy. you should know about what level of rdw is dangerous then You and your doctor need to be aware of potential health hazards so that they can be caught early and treated.
High RDW and Chronic Diseases
Increased RDW has been associated with a variety of chronic diseases. For example, cardiovascular disease is associated with an increased risk of heart failure and other cardiac events, and diabetes and metabolic syndrome are associated with disordered erythropoiesis. Inflammatory diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and chronic infections, may also alter RDW. Knowing What Level of RDW Is Dangerous and monitoring it can help detect complications early, even in people who are otherwise feeling well.
Lifestyle Tips to Maintain Healthy RDW (150 words)
- Eat a balanced diet that is rich in iron, B12, and folate
- Stay hydrated and don’t drink too much alcohol.
- Exercise regularly to maintain good health
- Control your chronic illnesses with the right medications and doctor visits
- Get regular blood tests – to keep an eye on RDW trends
Advanced RDW Insights
RDW has been demonstrated by recent research to forecast general health status, not just anemia. Prolonged elevation of RDW is also associated with increased risk of death and cardiovascular events. The RDW is not diagnostic by itself, however, it allows clinicians to use a useful marker to monitor patients over time.
Conclusion
RDW is an important indicator of red blood cell health. Elevated or decreased What Level of RDW Is Dangerous may be a sign of nutritional deficiencies, anemia or chronic illness. Although one abnormal result may not be cause for alarm, any abnormal results on a frequent basis should be considered a potential medical emergency. A healthy diet, managing chronic diseases, and talking to your doctor are important for a healthy RDW level. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and enhance general well-being.
People Also Asked (FAQ’s)
How long does RDW stay elevated or What Level of RDW Is Dangerous?
It depends on the underlying cause; deficiency states may normalize in a matter of weeks, chronic illness takes much longer to resolve.
Can lifestyle changes normalize in What Level of RDW Is Dangerous?
Yes, diet, supplementation and good disease management will improve RDW.
Can you fix a high RDW?
Often yes if due to nutriotional deficiencies or treatable diseases.
How often should I test RDW?
Your doctor may suggest testing every 3-6 months or with your routine blood work.
Can medications affect RDW?
Certain drugs influence the production of RBCs, and thus may slightly change RDW levels.